0:00-0:05
Welcome
In this video you’ll learn how to use the WhisperJECT Auto Injector device.
0:09-0:26
The WhisperJECT Auto-Injector is intended for use with FDA-approved drug products with non-viscous (aqueous) liquid formulations which are presented in a 1.0 milliliter BD®, pre-filled, glass syringe with staked needle, containing a fixed needle of 27G to 29G.
0:31-0:40
The WhisperJECT Auto-Injector is a reusable injection device for the subcutaneous injection of FDA-approved drugs.
WhisperJECT is available by prescription only.
0:43-0:50
It is important that you read the full instructions for use for the WhisperJECT Auto-Injector device that
are provided in the WhisperJECT packaging before use.
0:58-1:20
USE
GLATIRAMER ACETATE INJECTION is a prescription medicine that is used to treat relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS), to include clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease, in adults. It is not known if GLATIRAMER ACETATE INJECTION is safe and effective in children under 18 years of age.
1:21-1:28
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Do not take GLATIRAMER ACETATE INJECTION if you are allergic to glatiramer acetate or mannitol.
1:29-2:03
Serious side effects may happen right after or within minutes after you inject GLATIRAMER ACETATE INJECTION at any time during your course of treatment. Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these immediate post-injection reaction symptoms including redness to your cheeks or other parts of the body (flushing); chest pain; fast heartbeat; anxiety; breathing problems or tightness in your throat; or swelling, rash, hives, or itching. If you have symptoms of an immediate post-injection reaction, do not give yourself more injections until a healthcare provider tells you to.
2:09-2:35
Additional Important Safety Information is provided later in this video.
Before using GLATIRAMER ACETATE INJECTION, please read the Patient Information Leaflet and Instructions for Use found at the end of the full prescribing information for GLATIRAMER ACETATE INJECTION. The Prescribing Information came with your prescription and your welcome pack. This information does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment.
2:38-3:00
Viatris’ GLATIRAMER ACETATE INJECTION comes in individually wrapped pre-filled glass syringes. Keep your supply of syringes refrigerated at 36° to 46° Fahrenheit. If needed, you may store syringes at room temperature between 59° to 86° Fahrenheit for up to one month, but refrigeration is preferred.
3:03-3:07
Glatiramer Acetate is injected in the fatty layer under your skin.
3:12-3:28
You should receive your initial injection training and your first dose with your doctor or nurse present. Our patient support program, VIATRIS ADVOCATE, can schedule a follow-up, in-home injection training session with you with an MS experienced nurse should you need a refresher or have injection questions.
3:33-3:48
Before you inject gather your supplies, including your WhisperJECT Auto Injector device if your doctor
has prescribed it, alcohol wipe, cotton ball, needle clipper or sharps disposal container, one pre-filled glass syringe, and a place to record your injections.
3:51-3:58
Remove the syringe from the refrigerator about 20 minutes before injection and make sure it still has
the cap needle attached.
4:00-4:19
Wash your hands with soap and water and be careful not to touch your face or hair afterwards.
Choose a well-lit area of your home with a clean flat surface. Check the prefilled glass syringe for cracks
and check the solution for cloudiness or particles.
4:22-4:27
Do not try to remove any air bubbles from the syringe. This could cause you to lose some of your
medicine.
4:33-4:45
Choose an injection area from the seven possible areas shown, including the back of both upper arms,
the abdomen, the front of both thighs, and the back of both hips below the waist.
4:47-5:01
Choose a different injection area each time you inject. Each area has multiple injection sites. Do not
inject in the same site more than once a week.
Be sure to record the date and your injection site each time you inject.
5:04-5:19
Once you have chosen your injection site, you are ready to adjust the needle depth setting on the
WhisperJECT device.
To load the WhisperJECT twist the top and bottom of the device until the white arrows line up and pull
the device apart.
5:21-5:28
Place the device with the orange needle cap remover end up on a flat surface and hold it with one hand
for stability.
5:33-5:45
The WhisperJECT device is spring loaded. To set the spring, position the open end of the handle over the
needle cap remover and push the handle down until you hear a click then lift the handle up and off.
5:46-6:00
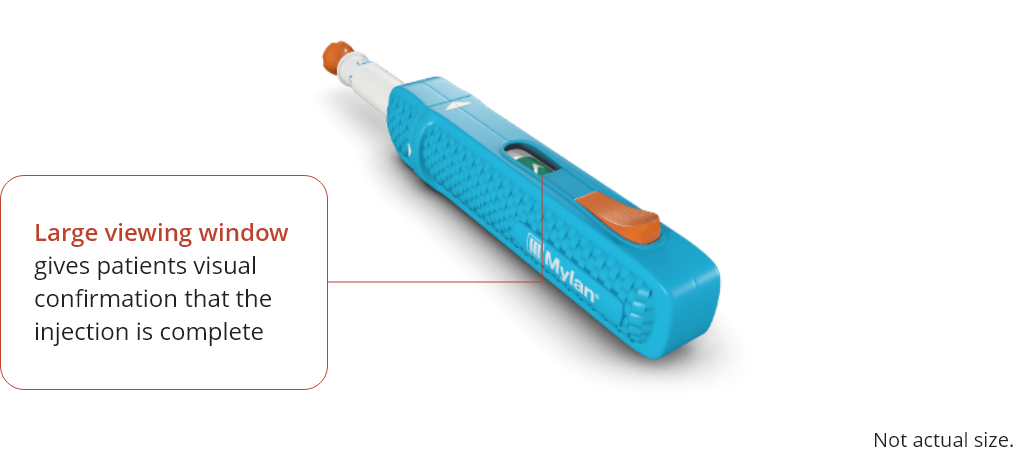
To confirm the auto injector is reset, a white check mark inside a green box will no longer be visible and
the plunger will occupy about half of the viewing window.
Also, the orange injection button will pop up.
6:05-6:17
Once the auto injector has been reset. Turn the depth adjuster until the depth you want lines up with
the blue semicircle.
Check with your doctor or nurse to determine your appropriate needle depth settings.
6:18-6:34
Sites in areas with more fatty tissue require a deeper injection and a higher depth setting,
such as 8 or 10 millimeters. In lean or muscular areas, you may need a lower depth setting, such as 4 or 6
millimeters.
6:39-6:43
Flip the syringe housing over so that the needle cap remover faces down.
6:49-6:58
Insert the glass syringe needle end first into the syringe housing. Firmly push down on the glass rim of
the syringe until it clicks into place.
7:04-7:18
Align the white arrows and twist the two parts of the device together.
Clean the injection site with an alcohol wipe and allow your skin to air dry. Be sure that your clothing is
not blocking the injection site.
7:20-7:23
Choose another injection site if the skin is scarred or dented.
7:25-7:38
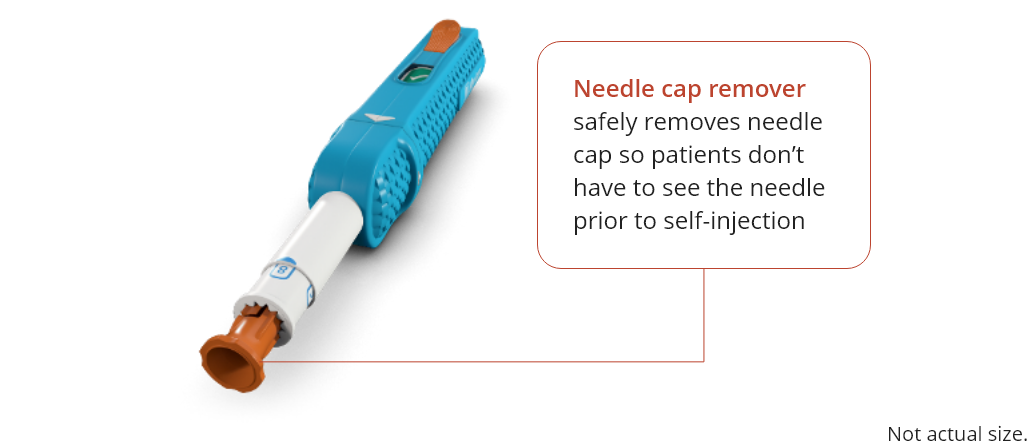
To remove the needle cap, hold the WhisperJECT device with one hand and firmly pull the orange needle
cap remover away from the device with your other hand.
It will come out with the needle cap inside.
7:50-7:59
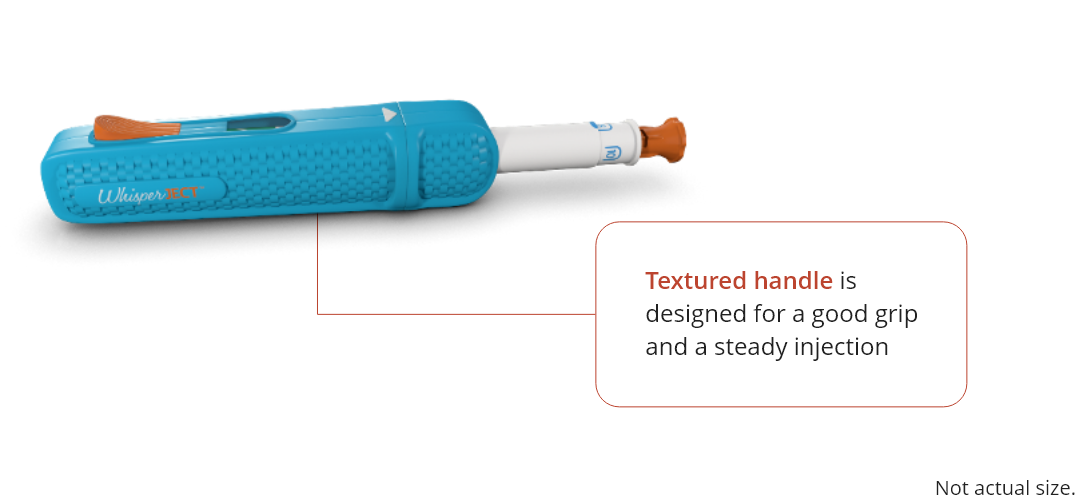
Grasping the device by the handle with the orange button comfortably within reach, place the auto
injector straight on the injection site, not at an angle.
8:00-8:11
Firmly push the auto injector down against your skin and hold in position when the needle depth
adjusters fully depressed, your device will be unlocked so that the orange injection button can be
pressed.
8:15-8:23
Press the orange injection button to start the injection, you will hear a click when the injection has
started. Make sure you can see the viewing window.
8:24-8:33
Continue to hold the auto injector down against the injection site, you will see green hash marks in the
viewing window as the medication is injected.
8:34-8:43
If you cannot see the viewing window, slowly count to 10 seconds after pressing the injection button
and hearing the first click. Do not lift up early.
8:46-8:57
When the injection is complete, a check mark will be fully visible in the window. Pull the WhisperJECT
away from your skin and apply a cotton ball to the injection site with gentle pressure.
8:58-9:07
Record the date and injection site in your injection journal or use the injection site Rotation plan available at our website glatirameracetate.com.
9:10-9:21
After injecting, carefully separate the two parts of your device. If you are using a needle clipper, clip the
needle and dispose of the clipper following local regulations when it is full.
9:24-9:32
Dispose of the used syringe in a Sharps disposal container. Then replace the orange needle cap
remover in its original location.
9:35-9:47
Your WhisperJECT device should be replaced after two years.
Please contact VIATRIS ADVOCATE to receive a replacement device at 1.844.695.2667.
9:48-10:03
For directions on using only the pre-filled syringe to self-inject and for information on anything you've
seen in this video, please see the Patient Information Leaflet and Instructions for Use at the end of the
Full Prescribing Information for Glatiramer Acetate Injection.
10:06-10:21
Please see Full Prescribing Information at www.GlatiramerAcetate.com.
You can also call VIATRIS ADVOCATE for instructions at 1-844-695-2667.
10:23-10:30
VIATRIS ADVOCATE Nurses are MS experienced and available to answer your injection
questions or concerns.
10:31-10:40
You can also schedule an in-home visit for one-on-one refresher injection training with the pre-filled
syringe or WhisperJECT device, if your doctor has prescribed it.
10:41-10:57
VIATRIS ADVOCATE nurses will also be more than happy to help you get started with your daily self-injections or to give you a refresher session if you've been on therapy for a while.
Please continue to watch for Important Safety Information about Glatiramer Acetate Injection.
11:01-11:22
USE
GLATIRAMER ACETATE INJECTION is a prescription medicine that is used to treat relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS), to include clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease, in adults. It is not known if GLATIRAMER ACETATE INJECTION is safe and effective in children under 18 years of age.
11:23-11:29
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Do not take GLATIRAMER ACETATE INJECTION if you are allergic to glatiramer acetate or mannitol.
11:30-12:05
Serious side effects may happen right after or within minutes after you inject GLATIRAMER ACETATE INJECTION at any time during your course of treatment. Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these immediate post-injection reaction symptoms including redness to your cheeks or other parts of the body (flushing); chest pain; fast heartbeat; anxiety; breathing problems or tightness in your throat; or swelling, rash, hives, or itching. If you have symptoms of an immediate post-injection reaction, do not give yourself more injections until a healthcare provider tells you to.
12:06-12:23
Chest pain may occur either as part of the immediate post-injection reaction or by itself. This type of chest pain usually lasts a few minutes and can begin around 1 month after you start using GLATIRAMER ACETATE INJECTION. Call your healthcare provider right away if you experience chest pain.
12:24-12:55
Damage to the fatty tissue just under your skin’s surface (lipoatrophy) and, rarely, death of your skin tissue (necrosis) can happen when you use glatiramer acetate injection. Damage to the fatty tissue under your skin can cause a “dent” at the injection site that may not go away. You can reduce your chance of developing these problems by:
- following your healthcare provider’s instructions for how to use glatiramer acetate injection
- choosing a different injection area each time you use glatiramer acetate injection
12:56-13:17
Liver problems, including liver failure, can occur with GLATIRAMER ACETATE INJECTION. Call your healthcare provider right away if you have symptoms, such as nausea, loss of appetite, tiredness, dark colored urine and pale stools, yellowing of your skin or the white part of your eye, bleeding more easily than normal, confusion, or sleepiness.
13:18-13:45
Some glatiramer acetate products can be used with an optional compatible autoinjector. Compatible autoinjectors are supplied separately if available, but the availability of compatible autoinjectors may change with time. Check with your healthcare provider when you fill or refill your medicine to make sure the autoinjector you have is meant to be used with your glatiramer acetate product. If you use the wrong autoinjector, you might not get the correct dose of your medicine.
13:46-14:32
The most common side effects in studies of GLATIRAMER ACETATE INJECTION are skin problems at your injection site, including redness, pain, swelling, itching, or a lump at the site of injection, rash, shortness of breath, flushing (vasodilation), and chest pain. These are not all the possible side effects of GLATIRAMER ACETATE INJECTION. For a complete list, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Tell your healthcare provider about any side effects that you have while taking GLATIRAMER ACETATE INJECTION.
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.






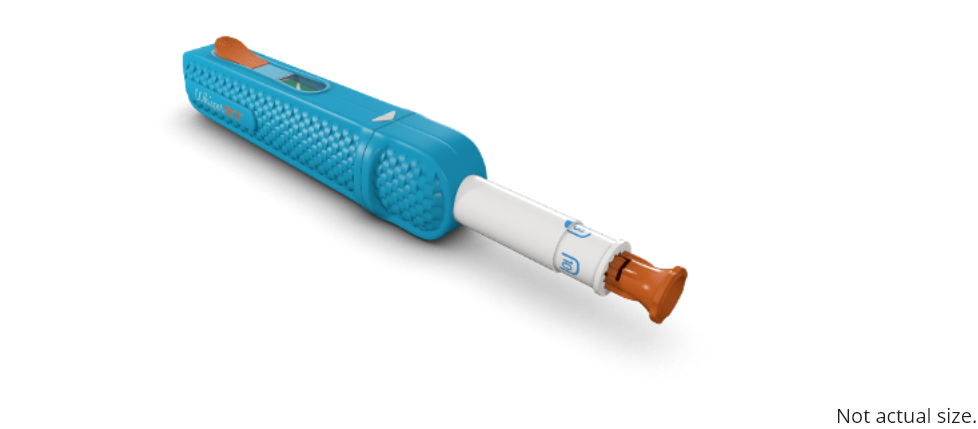

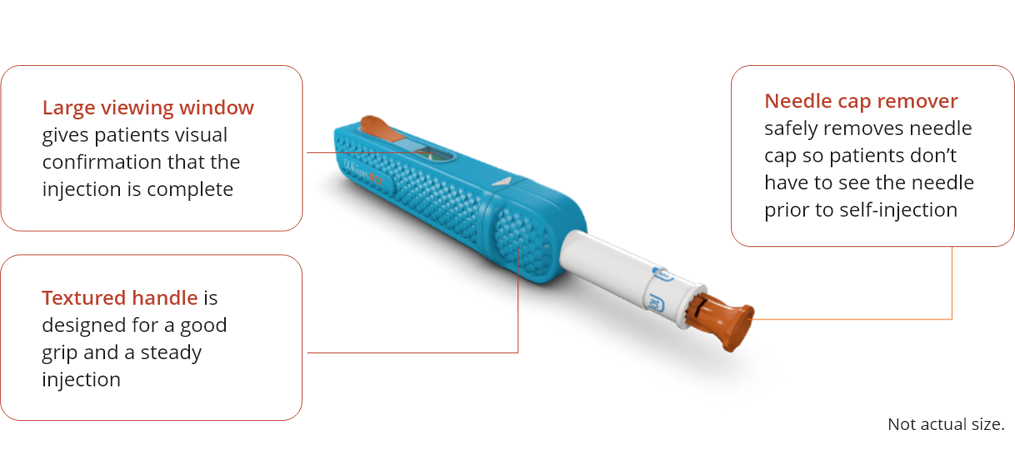
 Remove the syringe from its protective blister pack by peeling back the paper label.
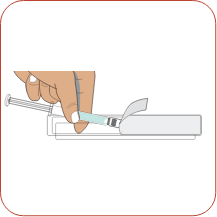
Remove the syringe from its protective blister pack by peeling back the paper label.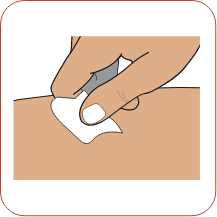 Choose an injection site on your body. Clean the injection site with a new alcohol wipe and let the site air-dry.
Choose an injection site on your body. Clean the injection site with a new alcohol wipe and let the site air-dry.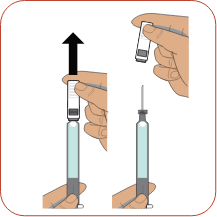 Pick up the syringe with one hand and hold it like a pencil. Remove the needle cap with your other hand.
Pick up the syringe with one hand and hold it like a pencil. Remove the needle cap with your other hand.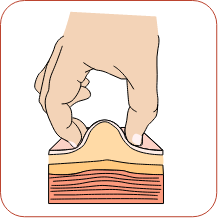 Pinch about a 2-inch fold of skin between your thumb and index finger.
Pinch about a 2-inch fold of skin between your thumb and index finger.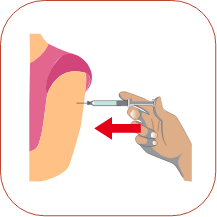 Rest the heel of your hand holding the syringe against your skin at the injection site. Insert the needle at a 90-degree angle straight into your skin. When the needle is all the way in, release the fold of skin.
Rest the heel of your hand holding the syringe against your skin at the injection site. Insert the needle at a 90-degree angle straight into your skin. When the needle is all the way in, release the fold of skin.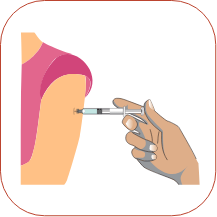 To inject the medicine, hold the syringe steady and slowly push down on the plunger.
To inject the medicine, hold the syringe steady and slowly push down on the plunger.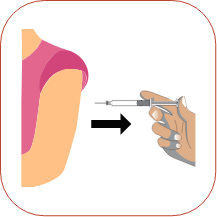 When you have injected all of the medicine, pull the needle straight out.
When you have injected all of the medicine, pull the needle straight out. Press a dry cotton ball on the injection site for a few seconds. Do not rub the injection site or re-use the needle or syringe.
Press a dry cotton ball on the injection site for a few seconds. Do not rub the injection site or re-use the needle or syringe.